[ad_1]
Let’s say that you’ve a world medical trial that reveals a brand new drug (SuperDrug) carry out higher than the earlier normal of care (OldDrug). Additionally assume that people with a selected comorbidity–let’s name it EF–reply much less properly to the SuperDrug therapy. When you stay in a rustic the place comorbidity EF is frequent, how properly do you suppose SuperDrug will work in your inhabitants?
That is the query posed by Turner et al. (2023) of their latest PharmacoEconomics paper. The overall downside nation decisionmakers face is the next:
When examine populations will not be randomly chosen from a goal inhabitants, exterior validity is extra unsure and it’s potential that distributions of impact modifiers (traits that predict variation in therapy results) differ between the trial pattern and goal inhabitants
Lots of you could have guessed that my comorbidity EF truly stands for an impact modifier. 4 lessons of impact modifiers the authors contemplate embrace:
- Affected person/illness traits (e.g. biomarker prevalence),
- Setting (e.g. location of and entry to care),
- Therapy (e.g. timing, dosage, comparator therapies, concomitant drugs)
- Outcomes (e.g. follow-up or
- timing of measurements)
See Beal et al. (2022) for a possible guidelines for impact modifiers.
Of their paper, the authors look at the issue of transportability. What’s transportability?
Whereas generalisability pertains to whether or not inferences from a examine could be prolonged to a goal inhabitants from which the examine dataset was sampled, transportability pertains to whether or not
inferences could be prolonged to a separate (exterior) inhabitants from which the examine pattern was not derived.
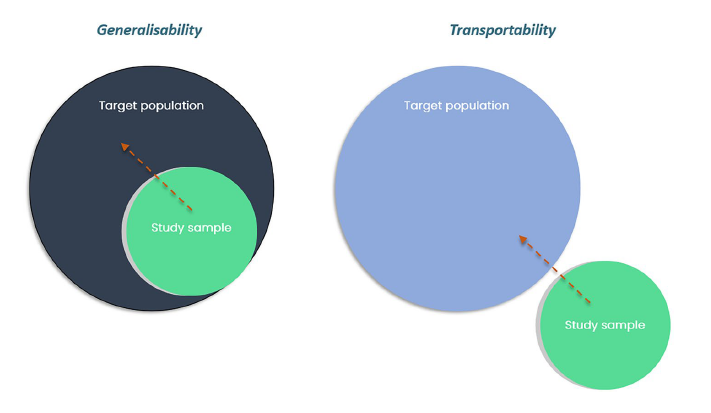
Key cross-country variations that will make transportability problematic embrace impact modifiers
resembling illness traits, comparator therapies and therapy settings.
What’s the downside of curiosity:
Usually, determination makers have an interest within the goal inhabitants common therapy impact (PATE): the common impact of therapy if all people within the goal inhabitants had been assigned the therapy. Nevertheless, researchers generally have entry solely to a pattern and should estimate the examine pattern common therapy impact (SATE).
Key assumptions to estimate PATE are included beneath:
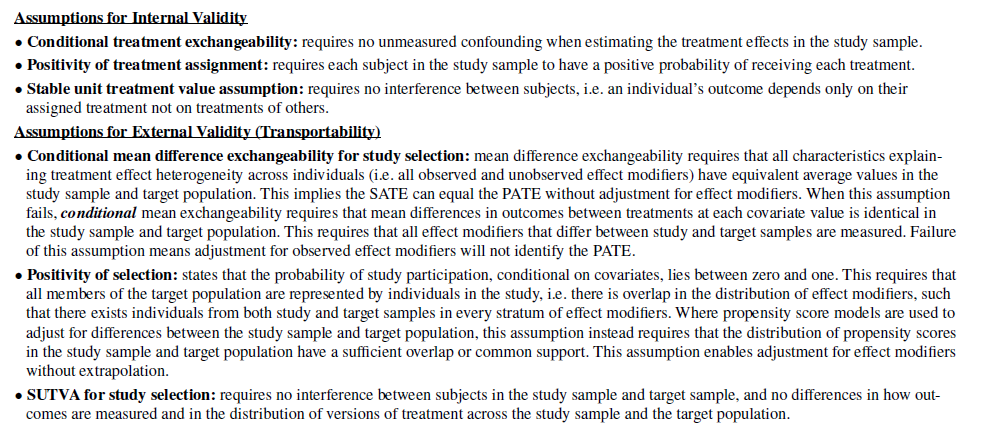
Primarily, there are two key objects to deal with (for RCTs at the least): (i) are there variations within the distributions of traits between examine and inhabitants of the goal nation/geography and (ii) are these traits impact modifiers [or for single arm trials with external controls, prognostic factors].
One can take a look at for variations within the distribution of covariates utilizing imply variations of propensity scores, inspecting propensity rating distributions, as properly formal diagnostic checks to establish the absence of an overlap. Univariate standardized imply variations (and related checks) can subsequently be used to look at drivers of total variations. If solely mixture information can be found, one could also be restricted to evaluating variations in imply values.
To check if a variable is an impact modifier, the authors suggest the next approaches:
Parametric fashions with treatment-covariate interactions can be utilized to detect impact modification. The place small examine samples lead to energy points or the place unknown useful
varieties improve the danger of mannequin misspecification, machine studying strategies resembling Bayesian additive regression timber may very well be thought-about, and the usage of directed acyclic
graphs could also be significantly essential for choosing impact modifiers on this case.
Approaches for adjusting for impact modifiers differ rely on whether or not a analysis has entry to particular person affected person information.
- With IPD: Use end result regression-based strategies, matching, stratification, inverse odds of participation weighting and doubly sturdy strategies combining matching/weighting with regression adjustment.
- With out IPD. Use population-adjusted oblique therapy comparisons (e.g., matching-adjusted oblique comparisons).
To find out which in-country information–sometimes real-world information–must be used because the goal inhabitants, one might contemplate quite a lot of instruments resembling EUnetHTA’s REQueST or the Knowledge Suitability Evaluation
Device (DataSAT) instrument from NICE.
You possibly can learn extra suggestions on how one can finest validate transportability points within the full paper right here.
[ad_2]