[ad_1]
Whereas most mortgage debtors are managing to pay down their money owed, a small however rising minority are experiencing monetary stress as they grapple with the pressures of the turbulent economic system.
Total, the Reserve Financial institution of Australia’s half yearly Monetary Stability Assessment launched on Friday confirmed Australia’s monetary system remained sturdy sufficient to deal with the difficult financial circumstances resembling inflation and cost-of-living pressures.
Nonetheless, debtors with low incomes, massive loans, and low financial savings are nonetheless at greater threat of mortgage stress and arrears.
Resilience amongst mortgage holders
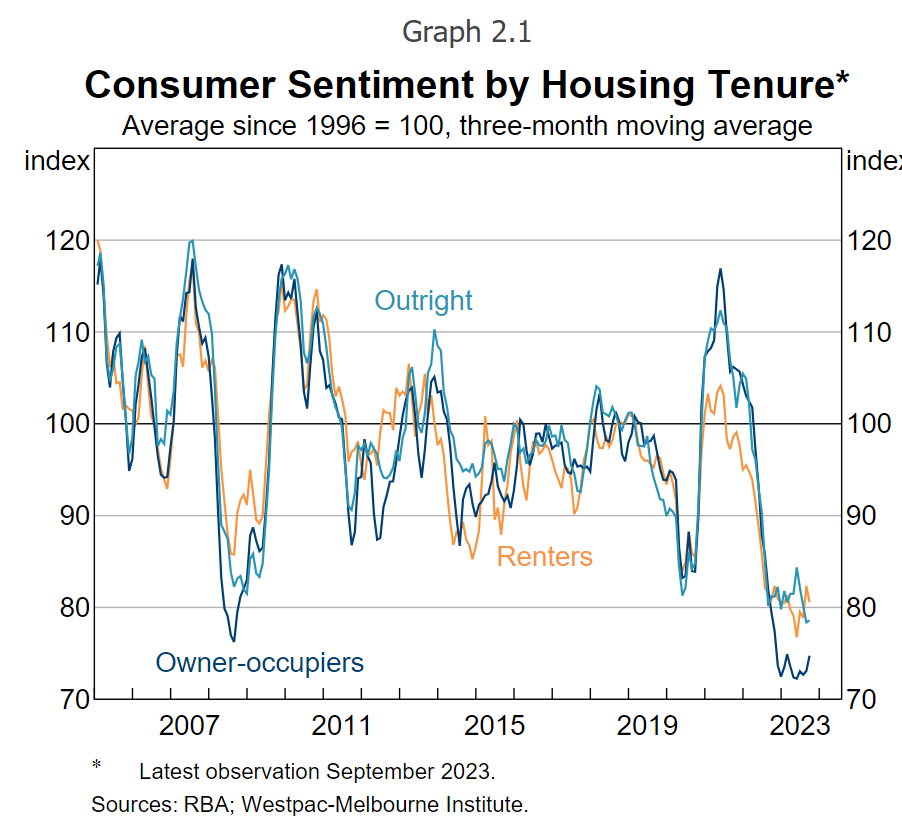
The place Australians as soon as had financial savings buoyed by the pandemic-era lockdowns and authorities stimulus, the assessment indicated greater rates of interest and inflation had decreased the spare money stream of most households.
Many households have been adjusting their expenditure, as evidenced by slowing consumption progress and sentiment of their present or future monetary well being had declined sharply since early 2022.
Through the use of the baseline family expenditure measure (HEM), the RBA discovered that 5% of Australian owners can’t cowl important bills, up from 1% final yr. These households are anticipated to have little capability to chop again on spending, the Monetary Stability Assessment discovered.
Nonetheless, the quantity jumps when checked out extra broadly by means of a HEM measure that features gadgets which might be classed as discretionary spending however may be tough to regulate, resembling non-public medical insurance and personal faculty charges.
By this measure, the share of variable-rate owner-occupiers whose bills and mortgage prices exceeded their revenue in July 2023 is estimated to be round 13%, up from round 3% in April 2022.
These debtors, nevertheless, are prone to have some capability to cut back spending over time.
Mortgage stress current however not widespread
Whereas this can be regarding, these debtors are usually not essentially in mortgage stress but as they could be dipping into financial savings or refinancing their loans. There’s additionally little proof that Australians are turning to bank cards or private loans to cowl their bills.
Most debtors are additionally anticipated to be effectively positioned within the occasion of an additional enhance in rates of interest.
The direct impact of a hypothetical 50 foundation level enhance within the money fee to 4.6% will increase the estimated share of variable-rate owner-occupier debtors who’re unable to cowl their bills (utilizing the baseline HEM) from round 5% to round 7%.
Of those debtors, about 30% are susceptible to depleting their buffers inside six months, which is equal to 2% of all variable-rate owner-occupier debtors.
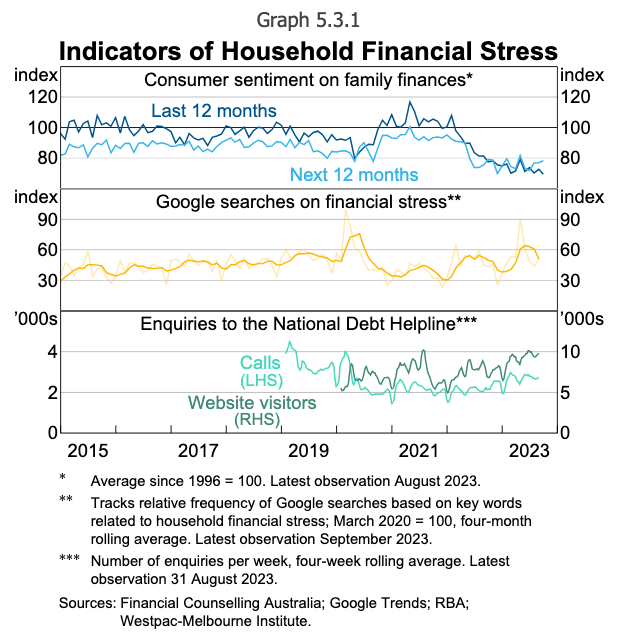
But the indicators are clear that monetary stress has entered the collective minds of Australians, with the frequency of Google searches of phrases associated to family monetary stress elevated earlier this yr to its highest degree for the reason that begin of the COVID-19 pandemic in early 2020.
Monetary counselling companies such because the Nationwide Debt Helpline has seen a 28% enhance within the variety of calls in comparison with final yr, which prompted ASIC to warn lenders about their monetary obligations in August.
That is additional corroborated by latest analysis from debtors, which had seen a 60% rise in debt information year-on-year and monetary hardship circumstances leap 25% over the quarter.
Insolvencies and mortgage arrears
On the opposite finish of the mortgage stress spectrum, private insolvencies and arrears have remained low regardless of a latest uptick. Hovering round 0.6% and 0.9% respectively, most households proceed to pay their money owed.
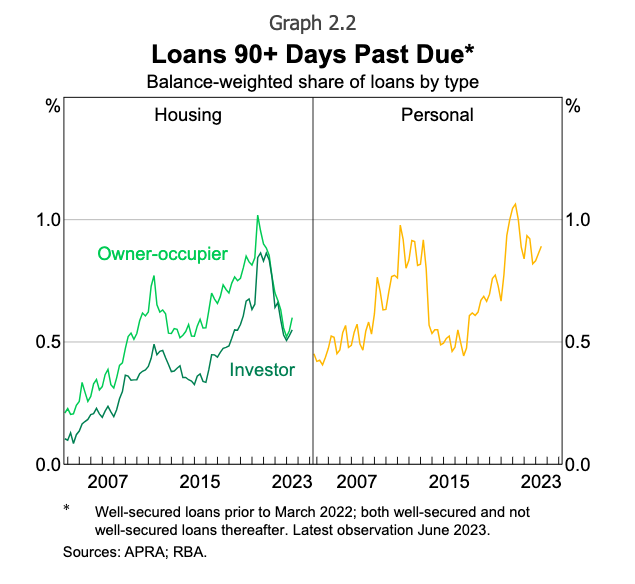
Lenders have reported that debtors have been extra resilient than anticipated of their capacity to service their debt, given the sharp rise in rates of interest. Whereas arrears charges are prone to enhance, they’re anticipated to stay very low.
About 1.5% of debtors are estimated to have their important bills and mortgage prices exceed their revenue and be at excessive threat of depleting any accessible buffers.
Even when the unemployment fee have been to extend by 2% – round twice as sharply as projected within the by the RBA in August – the share of current debtors susceptible to operating out of buffers over the following yr or so would possible stay at low single-digit ranges.
Equally, the RBA mentioned most debtors could be effectively positioned to service their housing loans if rates of interest have been to extend additional.
Get the most popular and freshest mortgage information delivered proper into your inbox. Subscribe now to our FREE day by day publication.
[ad_2]
