[ad_1]

Inflation within the U.S. has skilled unusually massive actions in the previous few years, beginning with a steep rise between the spring of 2021 and June 2022, adopted by a comparatively fast decline over the previous twelve months. This marks a stark departure from an prolonged interval of low and steady inflation. Economists and policymakers have expressed differing views about which components contributed to those massive actions (as reported within the media right here, right here, right here, and right here), resulting in fierce debates in coverage circles, tutorial journals, and the press. We all know little, nonetheless, concerning the client’s perspective on what brought about these sudden actions in inflation. On this publish, we discover this query utilizing a particular module of the Federal Reserve Financial institution of New York’s Survey of Shopper Expectations (SCE) by which shoppers had been requested what they assume contributed to the current actions in inflation. We discover that buyers assume supply-side points had been crucial issue behind the 2021-22 inflation surge, whereas they regard Federal Reserve insurance policies as crucial issue behind the current and anticipated future decline in inflation.
The SCE is a month-to-month, nationally consultant, internet-based survey of a rotating panel of roughly 1,300 family heads that has been performed by the New York Fed since June 2013. Along with its common month-to-month survey containing a hard and fast core set of questions, the SCE conducts occasional “particular surveys” of a subset of former SCE panelists fielded on an advert hoc foundation to deal with well timed policy-relevant questions. Right here, we concentrate on a particular survey fielded from June 7 to June 20, 2023, with 2,155 respondents. Within the survey, we requested respondents what they assume the twelve-month price of inflation was at three distinct closing dates: (1) earlier than the COVID-19 pandemic (in 2019), (2) over the twelve-month interval between June 2021 and June 2022, and (3) over the previous twelve months (between June 2022 and June 2023). As well as, we elicited respondents’ expectations for the speed of inflation over the following twelve months (between June 2023 and June 2024).
We used the responses for inflation perceptions and future expectations to ask tailor-made questions on which components respondents assume contributed to the modifications in inflation over three separate intervals: between 2019 and June 2022 (when precise inflation surged), between June 2022 and in the present day (when inflation began declining), and between in the present day and one 12 months from now. We introduced a listing of doable components and requested respondents to price the extent to which they consider every contributed (or will contribute) to the perceived (or anticipated) change within the price of inflation over a given interval utilizing a Likert scale between 1 (by no means vital) and 5 (crucial).
Beginning with the earliest interval, we discover that the majority respondents (80 %) assume that inflation rose between 2019 and June 2022. As proven within the chart under, the highest three components respondents rated as crucial contributors to the rise are all supply-related: “Product shortages and provide chain points,” “COVID-related shutdowns,” and “Employee shortages and staffing issues.” Specifically, 86 % of those respondents rated “Product shortages and provide chain points” as the best of the sixteen components they had been requested to price. This result’s according to the view that the surge in inflation over this era was resulting from binding capability constraints (see as an illustration right here). The relative consensus amongst shoppers that supply-side components had been the highest-rated contributors to the 2021-22 surge in inflation is sort of placing in comparison with the divergence of views that also seems to persist amongst economists and practitioners, talked about within the first paragraph above.
Significance of Elements in Contributing to the Inflation Enhance between 2019 and June 2022
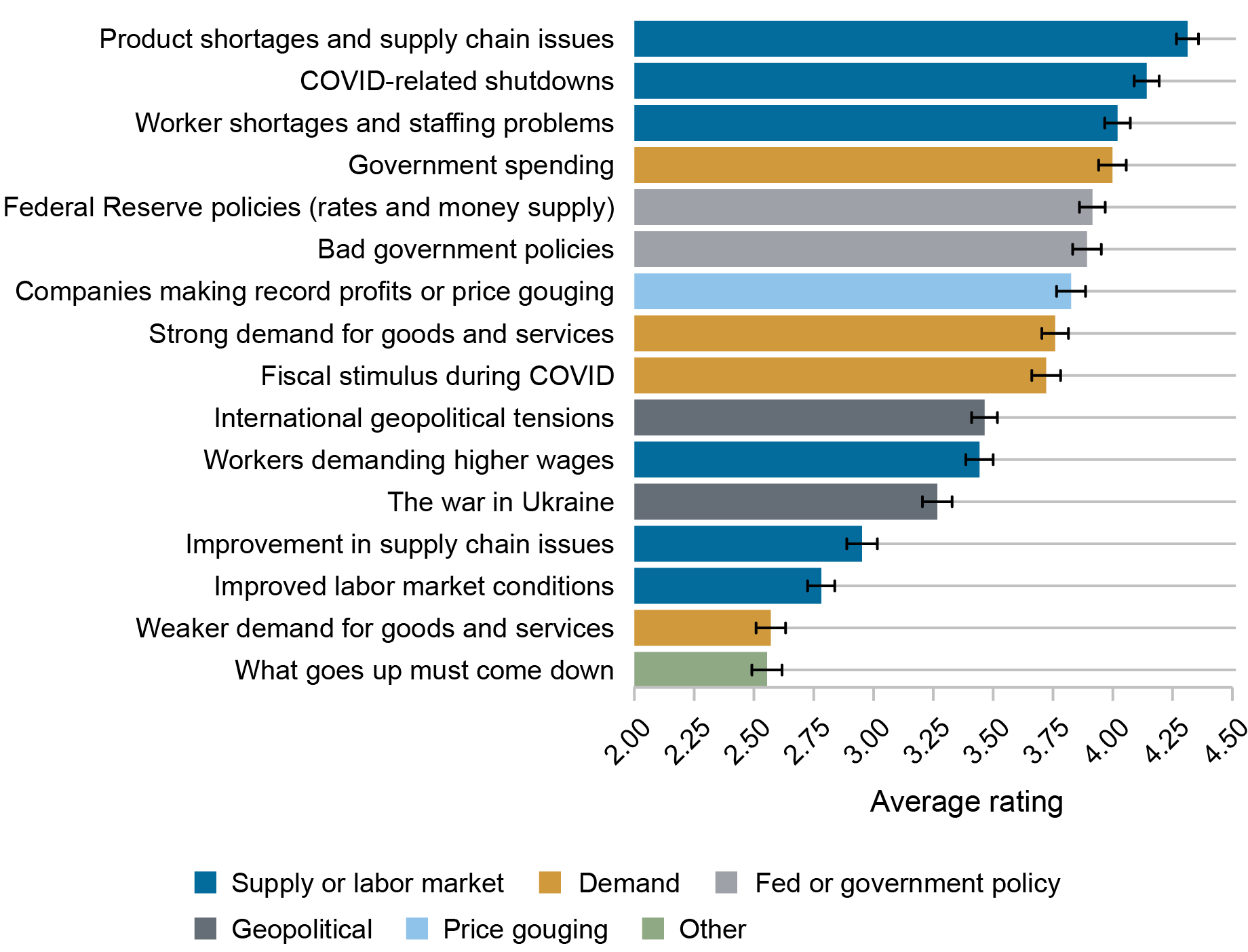
Supply: New York Fed Survey of Shopper Expectations.
Notes: The chart reveals the common significance score assigned to every issue as a contributor to the change in inflation among the many 1,698 respondents who perceived a rise in inflation between 2019 and June 2022. A score of 1 means “by no means vital” whereas a score of 5 means “crucial.”
The following three components ranked highest by shoppers within the chart above are a mix of demand-side and Federal Reserve or authorities insurance policies, indicating that buyers acknowledge that fiscal and financial coverage could have performed a job within the rise of inflation. The following issue, “Corporations making report income or worth gouging,” is ranked considerably decrease, maybe surprisingly in gentle of current discussions of doable “greedflation” and worth gouging (see as an illustration right here and right here). Equally, sturdy demand for items and providers and financial stimulus, which had been initially predicted to have massive impacts on inflation (see right here), weren’t ranked among the many most vital contributors to the rise in inflation—according to current findings. Lastly, regardless of its impression on oil and meals costs, shoppers rated the warfare in Ukraine as solely a modestly vital contributor to inflation over this era. A number of the impact, nonetheless, could have been captured by different components equivalent to “Product shortages and provide chain points.”
Turning now to the newest interval between June 2022 and June 2023, the chart under reveals that respondents who perceived a lower or a stabilization in inflation over the previous 12 months attributed this transformation at first to “Federal Reserve insurance policies (charges and cash provide),” adopted by “Enchancment in provide chain points.”
Significance of Elements in Contributing to the Inflation Lower between June 2022 and June 2023
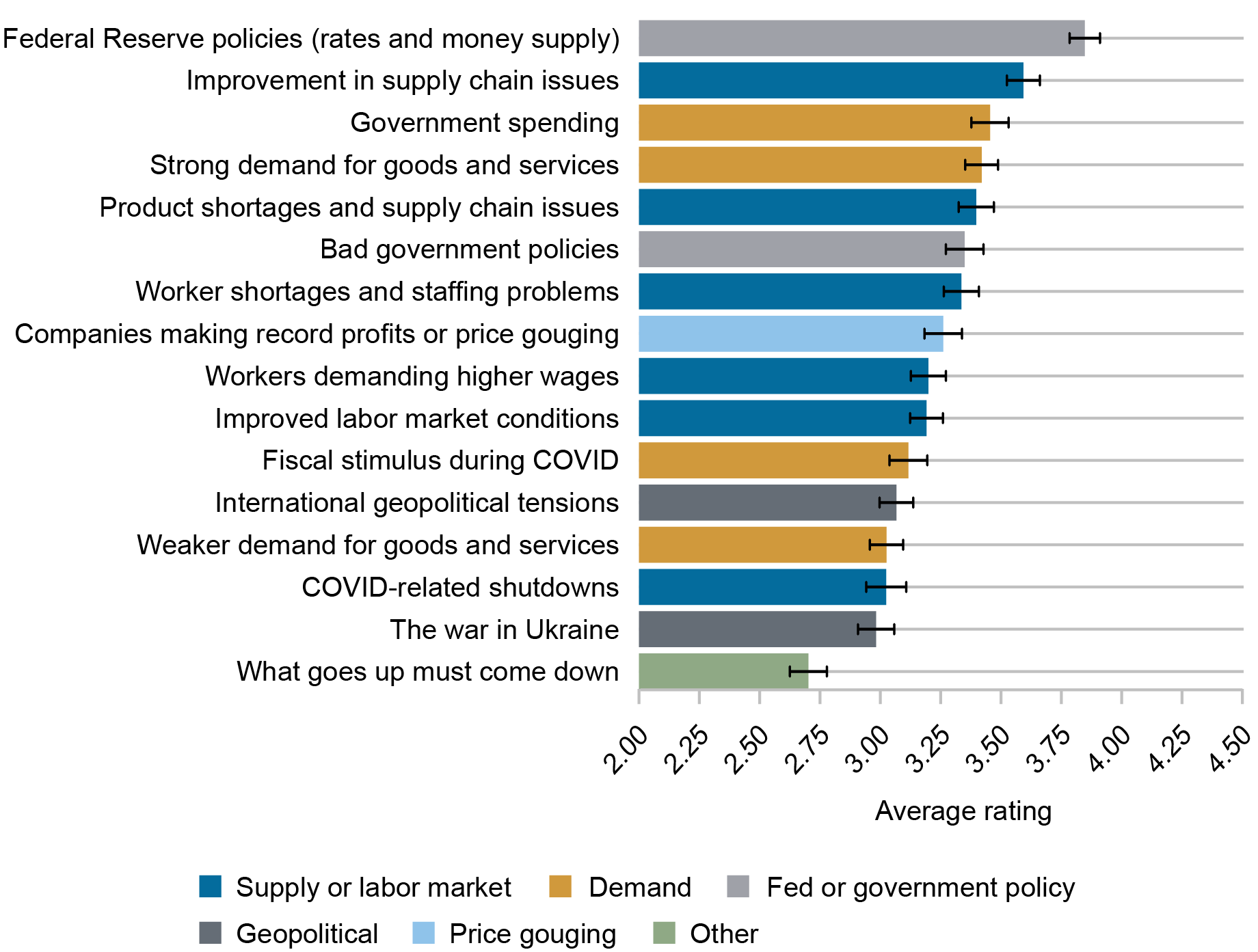
Supply: New York Fed Survey of Shopper Expectations.
Notes: The chart reveals the common significance score assigned to every issue as a contributor to the change in inflation among the many 1,171 respondents who perceived a lower or no change in inflation from June 2022 to June 2023. A score of 1 means “by no means vital” whereas a score of 5 means “crucial.”
The following chart reveals that the identical two components had been additionally ranked highest by the 82 % of respondents who anticipate a decline or a stabilization in inflation over the approaching 12 months.
Significance of Elements in Contributing to the Anticipated Inflation Lower between June 2023 and June 2024
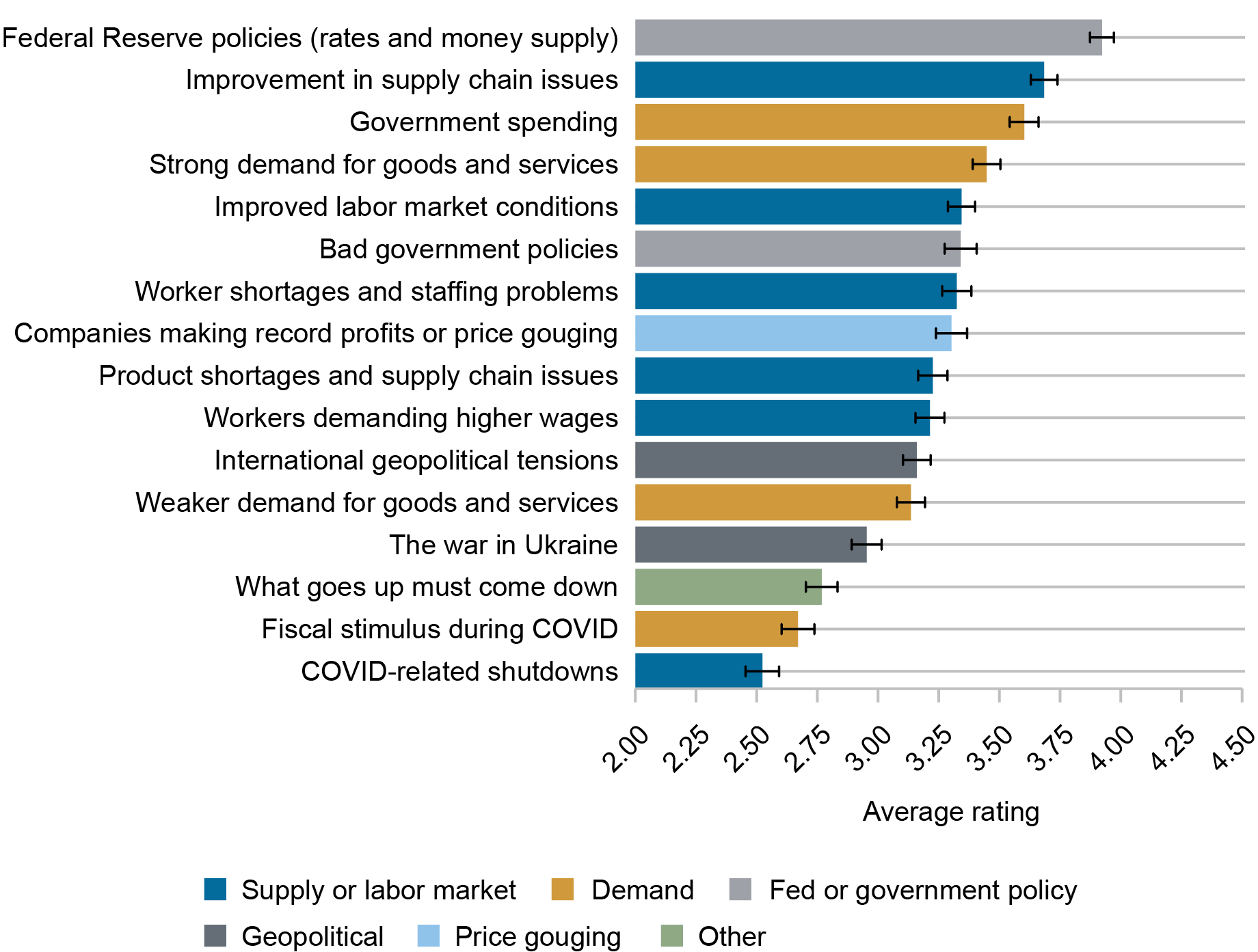
Supply: New York Fed Survey of Shopper Expectations.
Notes: The chart reveals the common significance score assigned to every issue as a contributor to the change in inflation among the many 1,744 respondents who anticipate a lower or no change in inflation between June 2023 and June 2024. A score of 1 means “by no means vital” whereas a score of 5 means “crucial.”
Our outcomes recommend that buyers consider provide chain points—a deterioration first adopted by enhancements—was among the many principal causes behind the sharp inflation actions the U.S. financial system has skilled since 2020. That buyers cite Federal Reserve insurance policies as crucial issue behind the current and anticipated future lower in inflation could seem at odds with current tutorial analysis at first. A number of research (see as an illustration right here and right here) recommend that American shoppers are typically imperfectly knowledgeable concerning the insurance policies of the Federal Reserve (for instance, they know little concerning the Federal Reserve’s inflation goal or ahead steering), which may restrict the effectiveness of financial coverage. Nonetheless, these research had been performed earlier than the surge in inflation of 2021, at a time when inflation was low and steady. The authors of those research acknowledge that in such an setting, shoppers could also be extra inattentive to inflation and financial coverage. In distinction, in intervals of excessive or altering inflation, shoppers could pay extra consideration to inflation and the actions of the Federal Reserve (for a current research displaying proof on this, see right here). Our outcomes present help to this speculation. Certainly, we discover that buyers in the present day know sufficient concerning the Federal Reserve to acknowledge its insurance policies as crucial issue behind the current and anticipated future decline in inflation.

Felix Aidala is a analysis analyst within the Federal Reserve Financial institution of New York’s Analysis and Statistics Group.

Olivier Armantier is the top of Shopper Conduct Research within the Federal Reserve Financial institution of New York’s Analysis and Statistics Group.

Fatima Boumahdi is a senior analysis analyst within the Financial institution’s Analysis and Statistics Group.

Gizem Kosar is a analysis economist in Shopper Conduct Research within the Federal Reserve Financial institution of New York’s Analysis and Statistics Group.

Devon Lall is a analysis analyst within the Federal Reserve Financial institution of New York’s Analysis and Statistics Group.

Jason Somerville is a analysis economist in Shopper Conduct Research within the Federal Reserve Financial institution of New York’s Analysis and Statistics Group.

Giorgio Topa is an financial analysis advisor in Labor and Product Market Research within the Federal Reserve Financial institution of New York’s Analysis and Statistics Group.

Wilbert van der Klaauw is the financial analysis advisor for Family and Public Coverage Analysis within the Federal Reserve Financial institution of New York’s Analysis and Statistics Group.
How you can cite this publish:
Felix Aidala, Olivier Armantier, Fatima Boumahdi, Gizem Kosar, Devon Lall, Jason Somerville, Giorgio Topa, and Wilbert van der Klaauw, “Shoppers’ Views on the Latest Actions in Inflation Expectations,” Federal Reserve Financial institution of New York Liberty Road Economics, August 17, 2023, https://libertystreeteconomics.newyorkfed.org/2023/08/consumers-perspectives-on-the-recent-movements-in-inflation-expectations/.
Disclaimer
The views expressed on this publish are these of the creator(s) and don’t essentially mirror the place of the Federal Reserve Financial institution of New York or the Federal Reserve System. Any errors or omissions are the duty of the creator(s).
[ad_2]
